Earthing, also known as grounding, is a fundamental component of electrical systems, ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical installations. It involves connecting parts of an electrical system to the ground, providing a path for fault currents to flow safely into the earth. This minimizes the risk of electrical shock, equipment damage, and fire hazards. Proper earthing is crucial for both industrial and residential electrical systems, and it requires precise methods and procedures for effective implementation.
The Importance of Earthing Systems
The primary purpose of an earthing system is to ensure safety. By providing a low-resistance path to the earth, it helps in dissipating fault currents, protecting both people and equipment from electrical hazards. Earthing systems also stabilize voltage levels, improving the overall reliability of the electrical network. Furthermore, they protect against electromagnetic interference, which can disrupt sensitive electronic devices.
Earth Testing Methods
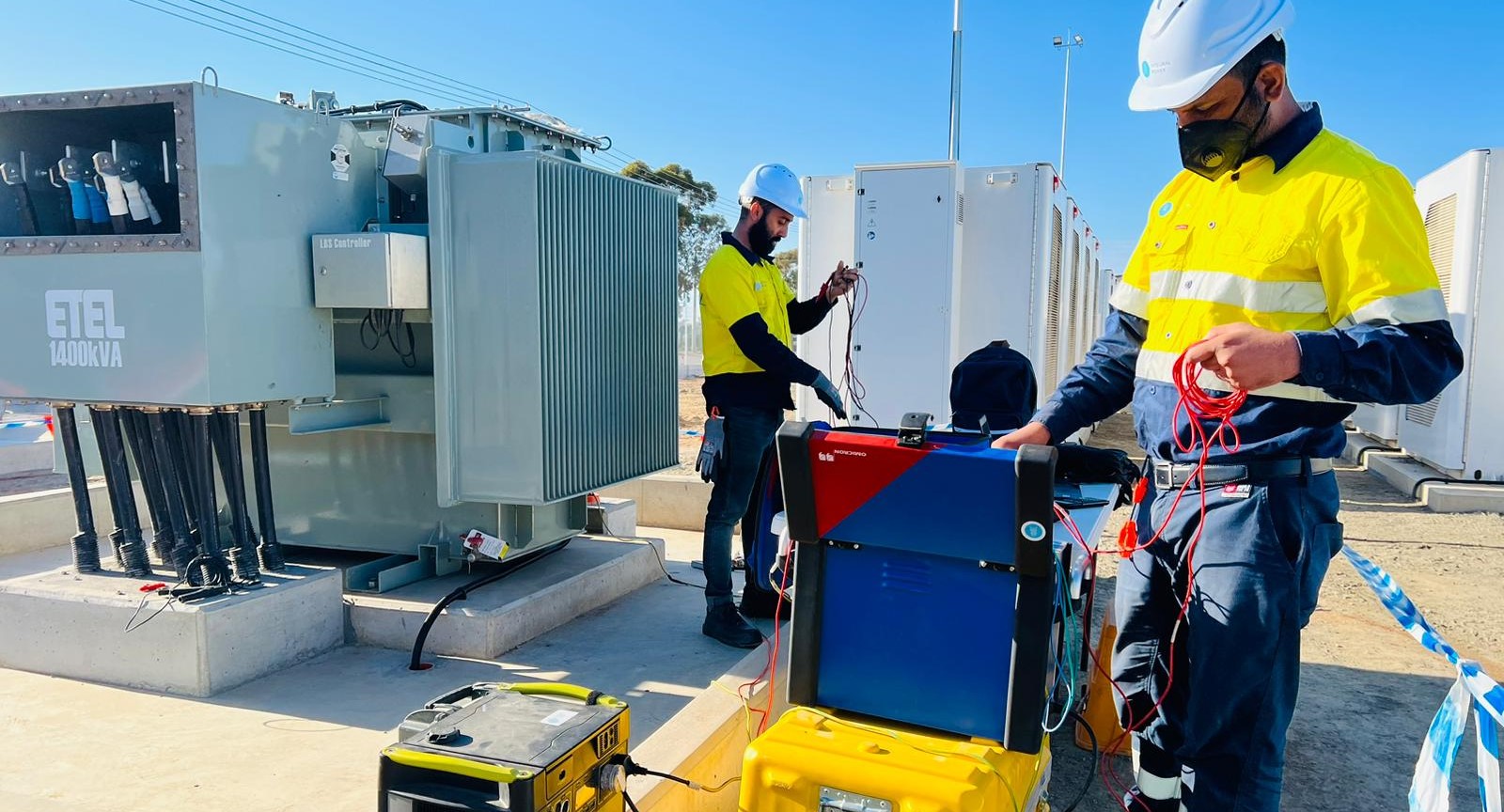
To ensure the effectiveness of an earthing system, regular testing is essential. Several methods are employed to assess the condition and performance of the earthing system.
Fall-of-Potential Method:
This is the most common method, which involves measuring the potential difference between two electrodes placed in the ground. By applying a known current to the earth through one electrode and measuring the voltage between the other two electrodes, the earth resistance can be calculated.
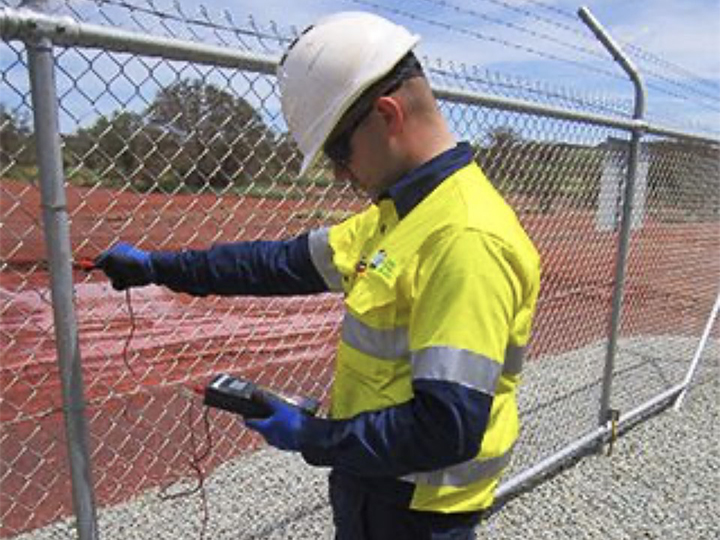

Clamp-On Testing:
This method is useful for testing earthing systems without disconnecting the earth electrode. A clamp meter is used to induce a current and measure the resistance. It is a convenient and non-intrusive method, often used for periodic maintenance checks.
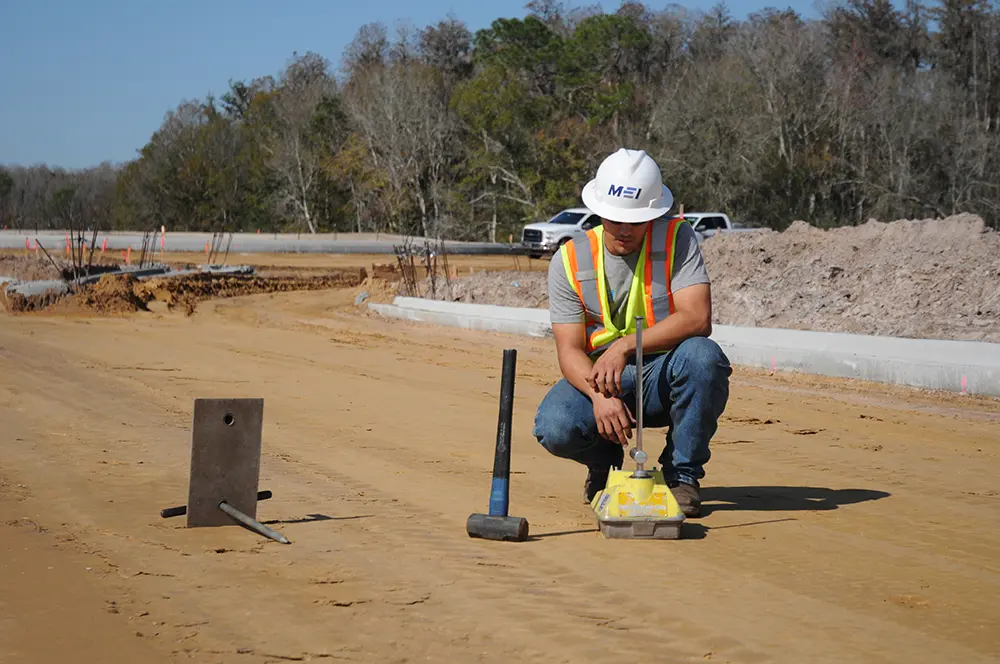
Soil Resistivity Testing:
Soil resistivity impacts the effectiveness of an earthing system. The Wenner four-pin method is commonly used, where four electrodes are placed in a straight line at equal distances. A current is passed through the outer electrodes, and the potential difference is measured between the inner electrodes to determine soil resistivity.
Earth Testing Procedure
Conducting an earth test involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Preparation:
Before testing, ensure all connections are secure and equipment is calibrated. Identify suitable locations for placing the test electrodes, considering factors like soil type and moisture content.
Electrode Placement:
For the fall-of-potential method, place the current electrode (C1) and potential electrode (P1) at specified distances from the earth electrode under test (E). Ensure the electrodes are inserted into the ground to a sufficient depth for accurate readings.
Testing:
Apply a known current through the current electrode (C1) and measure the potential difference between
the potential electrode (P1) and the earth electrode (E). Record the readings and calculate the earth
resistance using the formula;
R=IV
Where ( R ) is the earth resistance, ( V ) is the voltage measured, and ( I ) is the current applied.
Repeat and Verify:
Repeat the test at different distances to ensure consistency and accuracy of the results. Verify the readings against standard values and take corrective actions if necessary.

Earth Injection Testing
Earth Injection Testing is another important method, particularly for large-scale or complex earthing systems. This method involves injecting a high current into the ground and measuring the potential rise at various points. It provides a detailed analysis of the earthing system's performance under fault conditions.
Setup:
Connect a high-current injection device to the earthing system. Place potential measurement electrodes at strategic points to capture voltage rise during testing.
Injection and Measurement:
Inject a high current into the earthing system and measure the potential rise at the designated points. This helps in identifying any weak spots or areas of high resistance within the system.
Analysis:
Analyze the data to assess the performance of the earthing system. Ensure that the potential rise is within acceptable limits to guarantee safety and compliance with standards.
Role of an Electrical Earthing Consultant
Hiring an Electrical Earthing Consultant is crucial in electrical installations because they bring specialized expertise and experience to ensure the safety, reliability, and compliance of the earthing system. These consultants possess in-depth knowledge of regulatory standards and best practices, allowing them to design and implement earthing solutions that effectively mitigate electrical hazards. They conduct thorough site assessments, utilize advanced testing methods, and provide tailored recommendations to optimize the earthing system's performance. Additionally, they oversee the installation process and perform regular maintenance checks, ensuring the system remains effective over time.
Bottom Line
Overall, a well-designed and maintained earthing system is essential for the safety and reliability of electrical installations. Employing proper testing methods and procedures, such as the fall-of-potential method and earth injection testing, ensures that the system functions effectively.
Engaging an Electrical Earthing Consultant can provide expert guidance and ensure compliance with industry standards, ultimately protecting both people and equipment from electrical hazards.